Unit 10 - Origins
Content
Scheme of work
The Big Bang theory
The video below shows the relative sizes of the planets. moons, stars and galaxies in the known universe.
The big bang
Once the observation was made that everything in the universe appears to be moving away from everything else the logical conclusion was that all matter must have started out closer together.
The idea that everything started from one point in the universe and has been expanding ever since became known as the Big Bang.
The term originated during a radio broadcast in 1949 in which the astronomer Fred Hoyle was describing this theory of the origin of the universe.
Evidence for the Big Bang theory
The acceleration of galaxies that could be observed from Earth was determined by their Doppler shift. That is the shift in light wavelength due to their moving away from us. An object move towards us exhibits a compression of light waves making it seem more blue. An object leaving us at a great speed shows a stretching of the light waves and seems more red.
This effect is similar to the noise a train makes as it approaches compared to when it is moving away. During the approach the sound waves are compressed and the sound has a higher pitch. When moving away it has a lower pitch due to expansion of the sound waves.
The Doppler effect
The life-cycle of stars
Stars are thought to form from condensed gas being slowly collected by gravity until a critical mass is reached, when the object's gravity is powerful enough to allow the hydrogen atoms to fuse together. Several hydrogen nuclei are fused together in a series of steps forming Helium.
This fusion reaction releases vast amounts of energy.
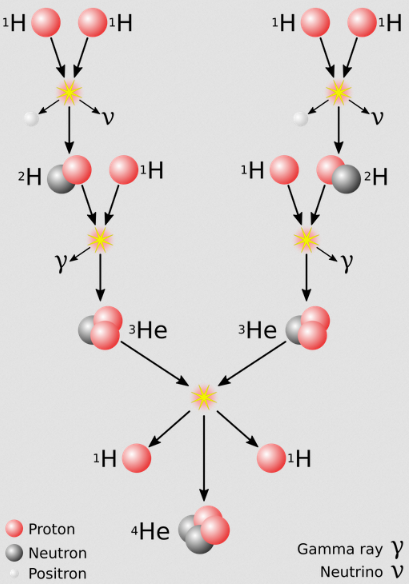
This is a simplified version. The video below explains about how stars go through different phases during their life cycle.
The life cycle of of stars.
What is a star made of
A star is made of gas, which consists mostly of Hydrogen and helium, the most commonly found elements in the Universe. The gas cloud is so dense its gravity holds it together.
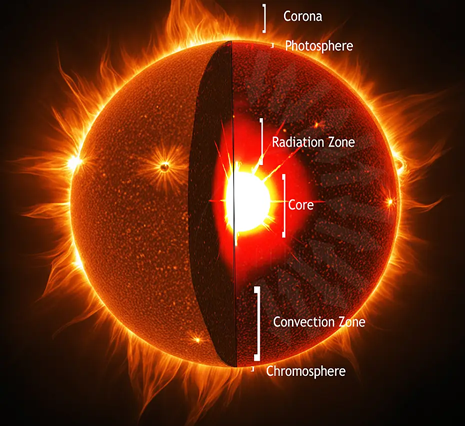
Like the Earth, stars are made of many layers, each with distinctive properties.
The structure of the sun
Stellar classification
Stellar classification, means the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines. Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that element. The strengths of the different spectral lines vary mainly due to the temperature of the photosphere, although in some cases there are true abundance differences.
The element helium was first discovered by examining the spectral lines of the sun. New coloured lines were discovered in the sun's spectrum that did not correspond to any known element on Earth. For this reason its name is helium, which comes from the Greek word "helios", meaning sun.
The spectrum of helium

The Earth
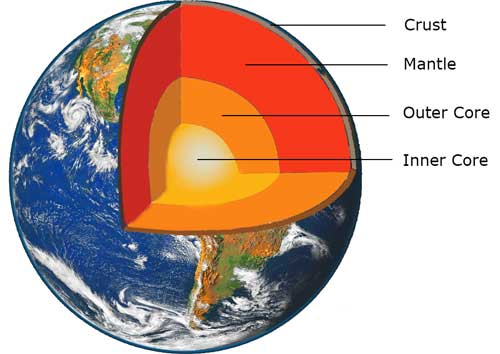
Our planet
The Earth consists of several well-defined layers. Evidence for this is obtained using sound waves. The inner-core consists of a solid nickel/iron alloy surrounded by a liquid of similar composition. Outside of this there is a large region of soft hot rock, known as the mantle. On the very outside is the Earth's crust on which the continents stand.
The moon

Classification of rocks
The lithosphere is the solid part of the Earth's crust. It consists of three types of rock:
- Igneous rock
- Sedimentary rock
- Metamorphic rock
The original form of the Earth was a molten ball of different substances condensed from the gasous remenants of exploded stars.
The lime cycle
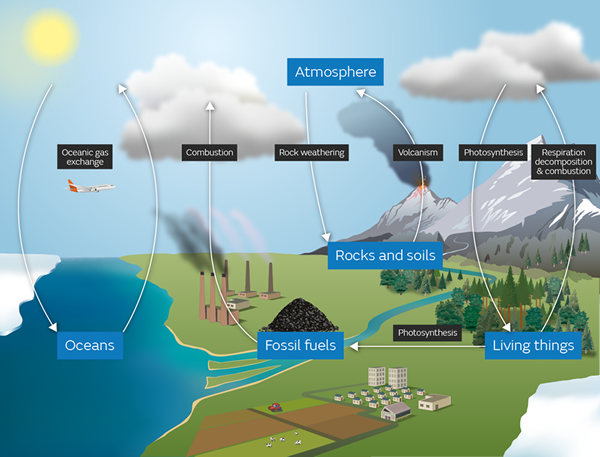
The carbon cycle
Carbon dioxide is intimately involved with the carbon cycle that you should already have studied.
Limestone
When the carbon cycle takes place in the sea, the organisms that die are decomposed by microorganisms and collect at the bottom of the sea as layers of skeletons made up of mainly calcium carbonate, CaCO3.
Over many years of geological time these layers of calcium carbonate become compressed and form a kind of rock called limestone.
As the sea-level changed over millions of years these layers of limestone appear once again as rock formations that may be pushed to thousands of metres of altitude.
Other layers of limestone get so compressed by the huge mass of rocks on top of them and the heat of the earth that the limestone changes to another form of calcium carbonate, called marble.
When calcium carbonate is heated strongly it decomposes, making calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Experimental - Action of heat on marble chips
You MUST take safety precautions in this experiment. Safety glasses and heat-proof mats.
- Place a small marble chip into a small test-tube half-full of water and add a few drops of Universal Indicator. Observe.
- With a second marble chip hold it in a pair of tongs and heat strongly in a Bunsen flame for about 5-10 minutes (it should glow white-hot)
- Drop the heated marble chip into a 100cm3 beaker half-full of water.
- Filter into a small conical flask.
- Divide into two samples.
- Sample 1 - add a few drops of Universal Indicator.
- Sample 2 - exhale gently using a straw through the sample.
- Make your observations
Study questions
- 1. Write out an equation for the decomposition of calcium carbonate.
- 2. What does the universal indicator test show you?
- 3. The word “decompose” appears twice in the introduction. Explain the similarities and differences between how the term is used.
- 4. Calcium oxide (quicklime) reacts with water forming calcium hydroxide (slaked lime). Write out an equation for this reaction.
- 5. Determine the mass of calcium oxide that can be formed by decomposition of 10g of calcium carbonate.
The lime cycle
This shows how calcium ions are implicated into the eco and geo systems of the world and interact wit the carbon cycle.
Carbon dioxide in the air dissolves in rainwater makine a slightly acidic solution (pH < 7). This solution of carbon dioxide is sometimes called carbonic acid due to the equilibria:
CO2(g) + H2O(l) ⇌ H2CO3(aq)
Some of the carbonic acid dissociates (breaks apart into ions) giving free hydrogen ions, which are responsible for acidity:
H2CO3(aq) → H+(aq) + HCO3-(aq)
This acidic solution can react with limestone, CaCO3, in the rocks making a dilute solution of calcium hydrogen carbonate, Ca(HCO3)2(aq)
CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) → Ca(HCO3)2(aq)
The resultant solution can pass through rivers to the sea, where it can be used by tiny sea organisms to build shell and bones. It is these creatures that over millions of years die, sink to the bottom of the sea and form layers of calcium carbonate that gets compressed into limestone.
If solutions of calcium hydrogen carbonate evaporate slowly, such as in caves, they can form stalactites and stalagmites in the caves, or even large crystals of calcite (see photo).
Ca(HCO3)2(aq) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
