1. Matter (particles and kinetic theory)
Knowledge and understanding
The kinetic theory of particles
All matter is particulate in nature. The energy of the particles is manifest as motion. The average energy is proportional to the absolute temperature.
The type of motion, distance, force between particles in solids, liquids and gases should be known.
The macroscopic volume and shape properties in solids, liquids and gases should be known.
Evidence for the particulate nature of matter:
- • Brownian motion
- • Diffusion
- • Dissolution
Changes of state.
The energy of the moving particles can overcome the forces that hold particles together. This results in a change of state
- • Melting
- • Boiling
- • Solidifying
Heating and cooling curves.
These demonstrate the energy changes that occur during the phase (state) changes associated with heating and cooling.

Pure substances and mixtures
A pure substance is made up of only one type of particle. The exception is ionic compounds, which are made up of giant structures that usually are made up of two oppositely charged ions in a regular lattice.
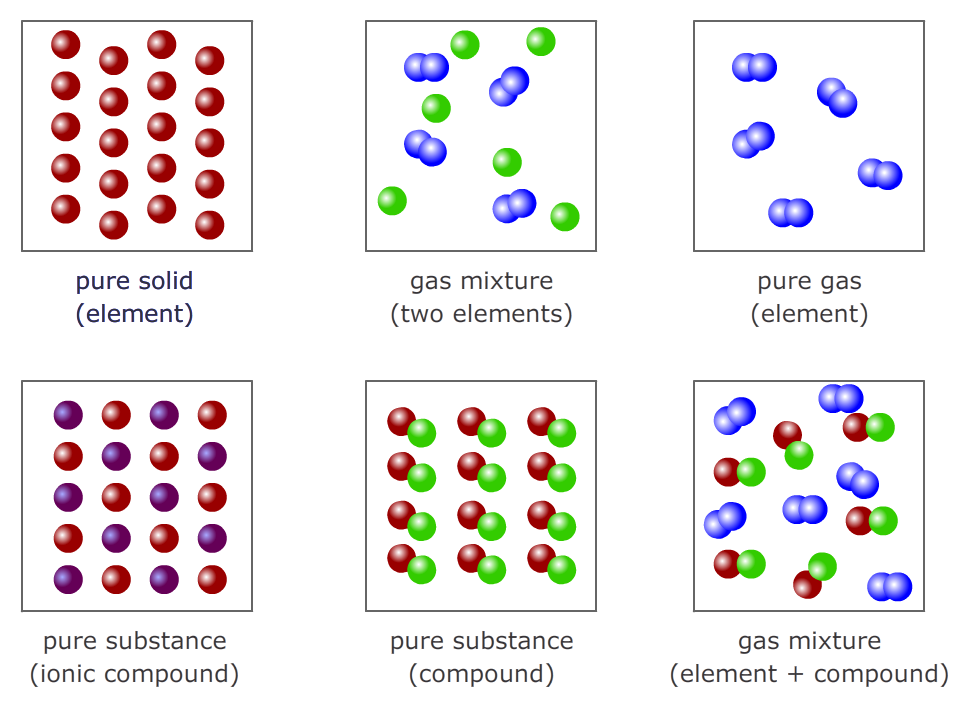
Separation of mixtures:
The following methods for separating mixtures should be known
- • Filtration
- • Distillation
- • Evaporation
- • Chromatography
- • Physical separation (e.g. magnet for iron and sulfur)
Skills
Recognise the state of matter from diagrams/descriptions of particles.
Suggest methods for separating given mixtures.
Explain the process of state change in terms of particles.
Book References
- States of matter: p.253
- Heating and cooling curves p.259
- Separation of mixtures p.484-491
2. Atoms (atomic structure and electron configuration)
Knowledge and understanding
Atoms have a tiny nucleus surrounded by negatively charges particles called electrons that move very fast. The Nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons.
The mass & charge properties of sub-atomic particles
- Atomic number = no. protons
- Mass number = sum (no. protons + no. neutrons)
- AZE atomic particle representation
Relative mass
Isotopes
Relative mass of elements.
Electronic arrangement in atoms
The electronic configuration first 20 elements
Skills
- Determine the number of sub-atomic particles from the AZE representation
- Determine relative mass from isotopic abundances
Book References
- The structure of the atom p.276-279
- Isotopes p.283-284
- Electron arrangement p.279-282
- Relative atomic mass p.311-312
3. Periodic table (trends, periods, groups)
Knowledge and understanding
Elements and compounds
An element is a structure made up of one type of atom.
There are about 90 naturally occurring elements
Periodic table
Elements arranged by atomic number, represented by symbol
Periods horizontal show number of energy shells
Groups with the same outer electron no.
Groups (1-8) vertical – new numbering system uses (1-18 and includes the transition metals)
Named groups
- • Group 1 - alkali metals
- • Group 2 - alkaline earth metals
- • Group 7 - halogens
- • Group 8 - noble or inert gases
Trends
Metals (left-hand side) make up the majority non-metals on the right-hand side
Metalloids show properties of both, zig-zag line
Groups show similarities of properties
Group 1
- • Reactive metals – more reactive going down the group
- • Low melting point – decreases down the group
Halogens
- • Reactivity increases going up – fluorine is most reactive element
- • Diatomic molecules, F2, Cl2 etc.
- • Toxic
- • Melting point increases down the group [F2, Cl2, Br2, I2, gases]
- • Coloured elements (pale yellow, green, red, violet)
- • Good oxidising agents (reactivity increases up the group)
d’ block metals – transition metals
- • Hard metals
- • High melting point
Noble gases
- • Monatomic
- • Full outer shells
- • Unreactive
Skills
Predict the properties of an element based on its position in the periodic table
Book References
- Periodic table p.399-401
- Groups and periods p.400-402
- Trends in groups p.400-404
- The alkali metals p.402-403
- The halogens p.403-405
- The noble gases p.406
4.1 - Bonding
Word and chemical reactions and formulas; acids, bases and pH
Knowledge and understanding
Formulas
Compounds are formed from different types of atom bonded together. They combine in specific ratios; this is known as the law of constant composition – every compound has a specific ratio of each atom called its formula.
Formulation
Use of subscripts in formulae. Valency ‘rules’.
Examples
- • Water, H2O
- • Common salt, NaCl
- • Ammonia, NH3
- • Methane, CH4
- • Sulfuric acid, H2SO4
- • Nitric acid, HNO3
- • Sodium hydroxide, NaOH
- • Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2
- • Glucose, C6H12O6
Chemical reactions
- • Synthesis: e.g.
- • Decomposition
- • Neutralisation
- • Redox
Reactants => products
Chemical Equations
The law of conservation of matter
Balanced equations
Coefficients
State symbols
Synthesis:
- • Metal + non-metal: Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl
- • Non-metal + non-metal: H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
Decomposition
• Thermal breakdown of carbonates: CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Neutralisation
- • Acid + base: NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
Redox
- • Metal + acid → salt + hydrogen
- • Inter-halogen reactions
Book References
- Formula p.303-306
- Chemical reactions p.355-357
- Neutralisation p.379-383
- Redox p.365
- Balanced equations p.308-309
4.2 - Acids, bases & pH
Knowledge and understanding
Definition of acids and bases
Arrhenius definition of acids – releases H+ ions in aqueous solution
Dissociation of simple mineral acids
pH scale [H+], 1-14
- • Acid pH 1-6
- • Base pH 8-14
Mineral acids
- • Sulfuric acid, H2SO4
- • Hydrochloric acid, HCl
- • Nitric acid, HNO3
Organic (weak) acid
- • Ethanoic acid, CH3COOH
Strong bases
- • Sodium hydroxide, NaOH
- • Potassium hydroxide, KOH
Weak base
- • Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2
Weak and strong acids
This does not refer to the concentration, rather to the nature of the compound. A strong acid dissociates (breaks apart) completely in solution into ions, whereas a weak acid only partially dissociates (maybe as little as 1%).
HCl(aq) ⇌ H+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
Indicators
Different colours in different pH solutions.
Neutralisation
Acids neutralise bases and vice versa: H+ + OH- → H2O
Reactions of acids
- Acid + base ==> salt + water
- Acid + metal carbonate ==> salt + water + carbon dioxide
- Acid + active metal ==> salt + hydrogen
Skills
- Recognise acidity from pH level
- Suggest compounds for neutralisation
- Write balanced equations for reactions of acids
Book References
- Acids, bases and salts p.376-379
- Indicators p.378
- pH scale p.378
- Alkalis and bases p.378
- Reactions of acids p.380
4.3 Bonding types
Knowledge and understanding
Simple covalent bonding
Structure
- • Shared electron pairs
- • Complete octets (full outer electron shells)
- • Non-metal to non-metal atoms
- • Small molecules
Properties (linked to structure)
- • Soluble in organic solvents
- • Poor solubility in water
- • Low melting point
- • Weak crystalline structure when solid
- • Non-conductor
Giant covalent bonding (macromolecular, network covalent)
Structure
- • Continuous covalent bonds from atom to atom
Properties (linked to structure)
- • Very high melting point
- • Very hard crystals (sand, diamond)
- • Insoluble
- • Non-conductors (exception graphite, graphene)
Examples
- • Silicon dioxide
- • Diamond
- • Graphite
Ionic bonding
Structure
- • Transfer of electrons
- • Formation of charged particles (ions) with full outer shells
- • Oppositely charged particles held together by electrostatic attraction
- • Giant structure
Properties (linked to structure)
- • Soluble in water (solute separates into solvated ions)
- • Hard brittle crystals
- • High melting point
- • Non-conductor when solid
- • Conductor in aqueous solution
- • Conductor when molten
Metallic bonding
Structure
- • Lattice of ions surrounded by ‘sea’ of delocalised electrons
- • Giant structure
Properties
- • Conductor
- • Usually high melting point (many exceptions)
- • Hard
- • Shiny
Skills
- Explain property of different substances by reference to the structure
- Recognise trends in property from given data
- Suggest bonding given property data
Book References
- Bonding p.284-292
- Metals, giant molecular structures p.293-294
- Alkali metals p402-403
5. Fuels (combustion)
Knowledge and understanding
Combustion and fuels
Fuels provide energy to do work (engines)
The fire triangle
Equations for combustion of hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbon + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
Source of fossil fuels
Fossil fuels (coal, oil and gas)
Conditions for formation of fossil fuels
- • Heat
- • Pressure
- • Anaerobic conditions
- • Geological time scale
Refining fossil fuels
Fractional distillation of crude oil
Use of the different fractions
- • Gas fraction – fuels
- • Petrol fraction – fuels
- • Kerosine – Aircraft engines
- • Diesel – Lorries, boats, heating
- • Lubricating oils – lubrication
- • Tar and Bitumen – road surfaces
Explanation of chain length and boiling point (link to covalent bonding)
Environmental concerns, global warming, depletion of resources
Electrical fuel cells
Lithium batteries
Energy density
Nuclear fuels - Fission
Environmental concerns, spent fuel storage, radioactivity
Skills
- Balancing equations for combustion of a given fuel
Book References
- Hydrocarbons p.454-455
- Fossil fuels p.230-231
- Combustion p.355,365
- Petrochemicals and polymers p.467-470
- Energy resources p.562-569
6. Electromagnetism (magnetism, magnetic fields; electric circuits)
Magnetism
Knowledge and understanding
Magnetic fields
Compasses
Earth’s magnetic field
Lines of force
North and south pole
Magnetic domains in ferromagnetism
Induced magnetism
Magnetic field around a current
Solenoid field
Electromagnetics
Magnetic interactions – magnet & magnet; motor effect and left-hand rule
Induced current caused by changing magnetic field
Transformers use and basic function.
Book References
- Magnetic fields p.668-671
- Magnetic forces p.668-671
- Electromagnetic induction p.669-671
Electric circuits
Knowledge and understanding
Circuit components and diagrammatical representation
- • Wires
- • Bulbs
- • Resistors
- • Meters
- • Power supply
- • Transformers
- • Solenoids
Units of potential difference, emf, voltage
Units of current
Flow of charge in coulombs
I = Q/t
Ohm’s law, I=PD/R (PD and R determine I)
Definition of resistance R=PD/I
How to use and ammeter and voltmeter
Current rules in series and parallel
PD rules in series and parallel
Book References
- Electrical circuits p.682-688
7. Forces and energy (motion, motion graphs, Newton’s laws; energy transfer and transformation)
Forces and Motion, motion graphs
Knowledge and understanding
Contact and non-contact forces (gravity, magnetic, electrostatic, tension, reaction, pushes and pulls)
Resistive forces (air vs friction)
Dynamic and static friction
Air resistance increases with speed
Vector quantities
Resolution of force vectors
Momentum
Newton's laws
Newtons first, second law (non-momentum version)
Inertia (mass= resistance to changes in motion)
Basic idea of third law (2 objects interacting cause a force)
Force acting on a body causes acceleration, F = ma
When the acceleration is that of gravity, we use the symbol, g, in which W = mg, where W = weight in newton.
Acceleration due to gravity alone is the same for all masses.
Distance - time graphs
Speed against time graphs
Interpretation of areas and gradients
Use of kinematic equations
- v= s/t
- a = (v-u)/t v = u +at
- v2 = u2 + 2as
- s=(v+u)t/2
Book References
- Forces p.529-534
- Describing motion p.520-528, 534-535
- Forces and matter p.570-574
Energy transfer and transformation
Knowledge and understanding
Energy
Units of energy
Forms of energy
Energy stores
- kinetic energy, KE = ½ mv2
- Gravitational potential energy
- Nuclear potential energy
- Electrical potential energy
- Chemical potential energy and internal energy related to state
- Magnetic potential energy
- Elastic potential energy
- Thermal energy (KE of particles) (internal energy)
Energy transfer
- • Conduction
- • Convection
- • Electromagnetic radiation including infrared
- • Gravitational potential to kinetic
- • Electrical to kinetic
- • Electrical to thermal
- • Electrical to chemical
- • Thermal to kinetic
- • Kinetic to thermal (by friction)
- • Kinetic to electrical
Factors that affect energy transfer
Everything ends up as heat (kinetic motion of particles)
Nothing is transferred with 100% efficiency, heat is always lost
Sankey diagrams
Particular explanation of conduction, convection
Everything ends up as heat (kinetic motion of particles)
Nothing is transferred with 100% efficiency, heat is always lost
Sankey diagrams
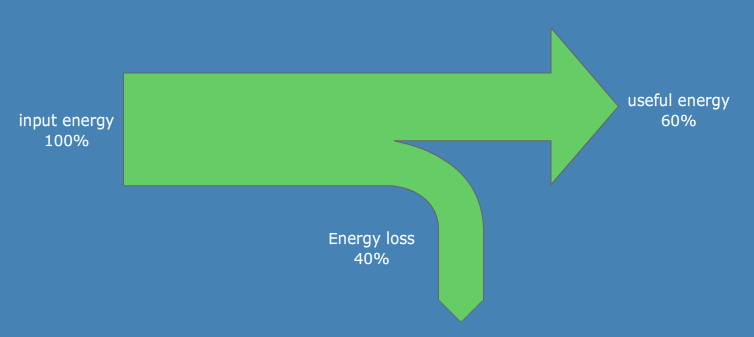
Skills
- Relate the Particle theory to explanations of convection and conduction
- Determine amounts of energy using simple equation.
- Determine the amounts of energy transfer given efficiency
- Determine the efficiency of energy transfer from transfer data
- Use of Work(W) = Fs
- Use of Gravitational potential energy (GPE) = mgh
- Use of Kinetic energy (K.E.) = ½mv2
- Use of Electrical energy(W) = IVt
- Use of Power (P) = E/t: P = IVt/t = IV: P = ΔKE/t: P = ΔGPE/t: P = W/t
Book References
- Energy transfer p.556-557
8. Waves (longitudinal and transverse waves, sound waves; wave phenomena including reflection, refraction, diffraction; wave equation; electromagnetic spectrum).
Knowledge and understanding
Skills
- Differentiating between wave types
- Wavelength, frequency, wave velocity and amplitude
- Laws of reflection and refraction
- The electromagnetic spectrum
Book References
9. Interactions between organisms (food chains and webs)
Knowledge and understanding
Environment
Habitats
Population
Community
Ecosystem
Food chains
Knowledge and understanding
Energy flow through food chains
Trophic levels
Classification of animals based on what they eat
Food webs
Knowledge and understanding
Energy flow through food webs
Human impact on food webs
Nutrient cycle
Skills
- Drawing food chain and food web
- Interpreting food chain and food web
- Interpreting graphs
Book References
- Interactions between organisms: environment, population, habitat, community, ecosystem
- p.225
- Food chains p.225
- Food web p.225
- Nutrient cycle p.230
- Carbon cycle p.230
10. Metabolism (digestion, gas exchange)
Digestion
Knowledge and understanding
Nutrients
Carbohydrates
Fats
Protein
Digestion
Enzymes
Skills
- with enzymes: sketching shapes and interpreting graphs
Book References
- Biological molecules p.31-39
- Enzymes and factors that affect them p.41-45
Gas exchange
Knowledge and understanding
Aerobic respiration
Anaerobic respiration
Gas exchange (diffusion)
Effect of exercise on the breathing rate
Factors affecting human health: smoking
Skills
Balancing chemical equations
Interpreting graph data such as incidence of cancer in smokers.
Book References
- Biological molecules p.31-39
- Enzymes and factors that affect them p.41-45
- Respiration (aerobic and anaerobic) p.142-144
- Gas exchange p.173
- Diffusion p.17-18
- Effect of exercise on breathing rate p.141-142
11. Systems (photosynthesis and respiration)
Living systems
- • Reproduce
- • Move
- • Expel waste matter
- • React to stimuli
Photosynthesis
Knowledge and understanding
Cells, tissues, organs and systems
Plant cell
Transport in plants
Osmosis
Photosynthesis equation
Skills
Balancing chemical equations
Book References
- Diffusion p.17-19
- Osmosis p.20-24
- photosynthesis p.54
- Plant cell p.4
- Cells, tissues, organs p.9-10
12. Cells (tissues, organs and systems; cell division; reproduction)
Cells and tissues
Skills
Draw cells scientifically and label them correctly
Book References
- Microscopes p.3
- Living processes p.2
- Cell structure p.5,6
- Movement in and out of cells/tissues p.10-16
Organs
Skills
Identify organs by function and position in the human body.
Book References
- Human reproductive organs p.137
- Heart p.79
- Human gas exchange system p.94
- Human digestive system p.58
Cell division
Knowledge and understanding
Understand the purpose of cell divison
Understand what happens in each phase and why
Skills
Recognising what phase the cell division process is in.
Compare the two methods of division.
Book References
- Mitosis p.196-197
- Meiosis p.197-198
Reproduction
Knowledge and understanding
Identify and give the functions of the reproductive organs.
Understand how fertilisation happens.
Understand the roles of hormones in the menstrual cycle.
Skills
Label scientific diagrams correctly
Book References
- Female reproductive organs p.178
- Male reproductive organs p.179
- Fertilisation p.180-181
- Menstrual cycle p.182-183
Exam Practice - MYP Self-Test